Josh Boak and Emily Swanson | The Associated Press
October 1, 2021
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden’s popularity has slumped after a slew of challenges in recent weeks at home and abroad for the leader who pledged to bring the country together and restore competence in government, according to a new poll by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research.
Fifty percent now say they approve of Biden, while 49% disapprove. Fifty-four percent approved in August, and 59% did in July. The results come as Americans process the harried and deadly evacuation from Afghanistan, mounted border patrol agents charging at Haitian refugees, the unshakable threat of the coronavirus with its delta variant and the legislative drama of Biden trying to negotiate his economic, infrastructure and tax policies through Congress.
Since July, Biden’s approval rating has dipped slightly among Democrats (from 92% to 85%) and among independents who don’t lean toward either party (from 62% to 38%). Just 11% of Republicans approve of the president, which is similar to July.
Approval also dipped somewhat among both white Americans (49% to 42%) and Black Americans (86% to 64%).
In follow-up interviews, some of those who had mixed feelings about Biden’s performance still saw him as preferable to former President Donald Trump. They said that Biden was dealing with a pandemic that began under the former president, an Afghanistan withdrawal negotiated on Trump’s behalf and an economy that tilted in favor of corporations and the wealthy because of Trump’s tax cuts.
“Trump had a lot to do with what’s going on now,” said Acarla Strickland, 41, a health care worker from Atlanta who voted for Biden yet now feels lukewarm about him.
As a mother of four, Strickland said she has benefited from the monthly child tax credit payments that are flowing as part of Biden’s $1.9 trillion coronavirus relief package. But she feels the government needs to do more to help Americans. Strickland said she borrowed $66,000 to get a master’s degree and fears the debt will never be repaid.
Just 34% of Americans say the country is headed in the right direction, down from about half who said that through the first months of Biden’s presidency. Trump supporters such as Larry Schuth feel as though Biden is damaging the nation by seeking to enlarge government and mismanaging the southern border. The Hilton, New York, resident added that he would like to travel to Canada but can’t because of COVID-19 restrictions.
“If he had a plan to destroy this country and divide this country, I don’t know how you could carry it out any better,” said Schuth, 81. “We’re spending way too much money. We’re planning on spending even more. We don’t have a southern border.”
The poll shows that 47% of Americans approve of how Biden is handling the economy, down from a high of 60% in March but similar to where it stood in August.
The initial burst of optimism from Biden’s rescue package has been met with the hard realities of employers struggling to find workers and higher-than-expected inflation as supply chain issues have made it harder to find automobiles, household appliances and other goods. The rise of the delta variant and reluctance by some Americans to get vaccinated also slowed hiring in August.
Roni Klass, a tutor in her 70s living in Miami, said she was glad to vote Trump out, but she’s worried about inflation given her dependence on Social Security and wages that have yet to rise.
“When I go to the grocery store, the prices have really shot up,” she said. “My money coming in is not keeping up with the money that I have to spend going out, and I have to cut back as much as I can.”
The poll finds 57% approve of Biden’s handling of the coronavirus pandemic. That number is similar to August but remains significantly below where it stood as recently as July, when 66% approved. Still, it remains Biden’s strongest issue in the poll. Close to 9 in 10 Democrats approve of Biden’s handling of the pandemic, compared with about 2 in 10 Republicans. In July, about 3 in 10 Republicans said they approved.
More also approve than disapprove of Biden’s decision to require that most U.S. workers be vaccinated or face regular testing, 51% to 34%, with 14% saying they neither approve nor disapprove. About 8 in 10 Democrats approve; roughly 6 in 10 of Republicans disapprove.
Biden struggles on several issues related to foreign policy. Forty-three percent say they approve of his handling of foreign policy overall, and only 34% approve of his handling of the situation in Afghanistan. Even among Democrats, only 54% say they approve of Biden’s handling of Afghanistan. Just 10% of Republicans say the same.
At the same time, Americans are slightly more likely to approve than disapprove of the decision to remove the last remaining U.S. troops from Afghanistan at the end of August, with 45% saying they approve of that decision and 39% saying they disapprove. About two-thirds of Democrats approve of the decision to withdraw troops, compared with about a quarter of Republicans. Roughly two-thirds of Republicans disapprove.
Forty-six percent of Americans approve of Biden’s handling of national security, while 52% disapprove.
The poll was conducted just after tensions emerged with France over a submarine deal with Australia, but it finds 50% approve of how Biden is handling relationships with allies — similar to his approval rating overall.
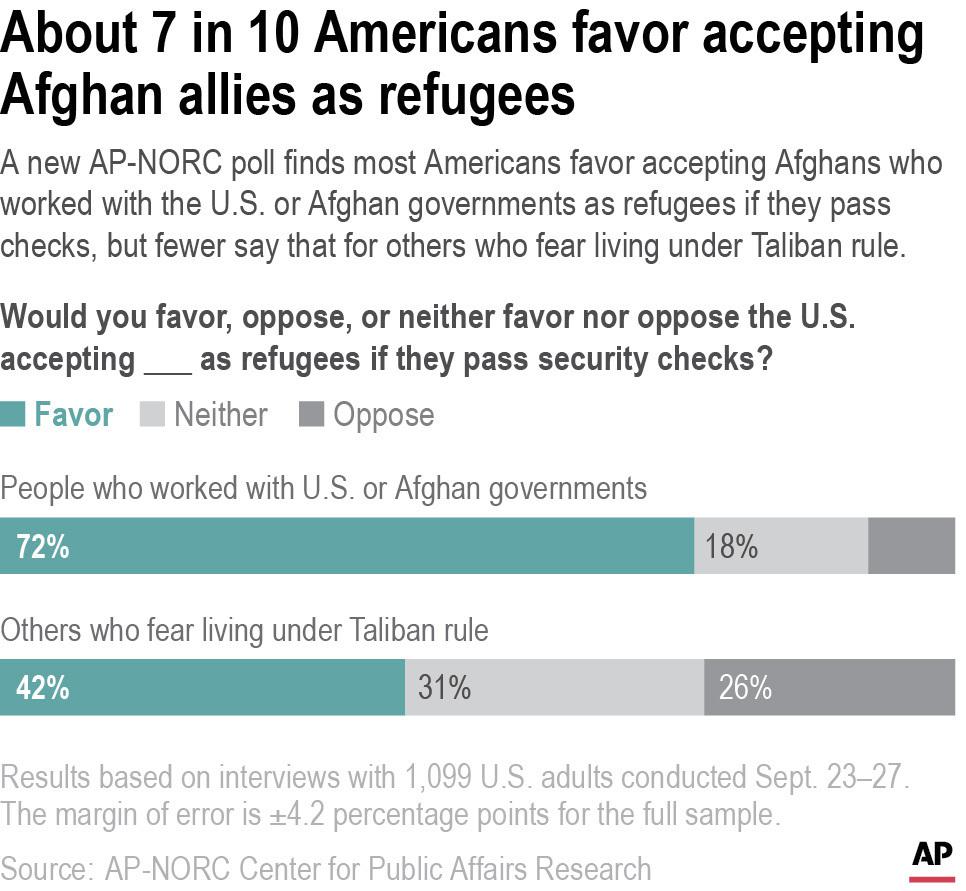
Just 35% of Americans approve of Biden’s handling of immigration, down from 43% in April, when it was already one of Biden’s worst issues. Immigration is a relative low point for Biden within his own party with 60% of Democrats saying they approve, along with 6% of Republicans.
The president has committed himself toward humane immigration policies, yet the persistent border-crossings and flow of refugees from Haiti and Afghanistan has led to challenging debates and troubling images. Immigration poses a challenge because voters are divided over whether to welcome more foreigners or focus the government more on the needs of existing citizens.
“There isn’t enough money to take care of our own, why do we have to take care of some other country?” said Anthony Beard, 48, a chef from Lansing, Michigan.
___
The AP-NORC poll of 1,099 adults was conducted Sept. 23-27 using a sample drawn from NORC’s probability-based AmeriSpeak Panel, which is designed to be representative of the U.S. population. The margin of sampling error for all respondents is plus or minus 4.2 percentage points.